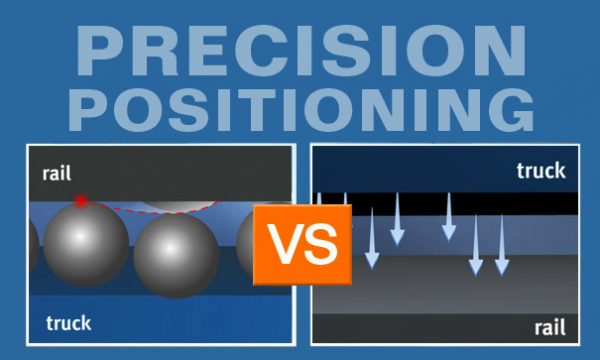
When your application requires precision positioning, it is important to understand that rails and guideways often exhibit flatness deviations. Some of these are inherent…others may develop over time. Either way, the momentum of the balls in a rolling element bearing actually amplify the unwanted motion of the bearing. In fact, rail-ball contact further damages both…
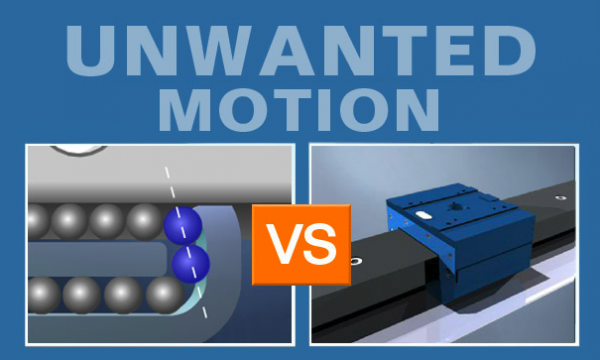
Unwanted Motion
A direct comparison of porous media air bearings and conventional rolling element bearings shows that, when using the latter, there is a significant amount of unwanted motion in all directions. This is because there are minute differences in the size of the balls themselves and the balls are also slightly larger then the clearance in…
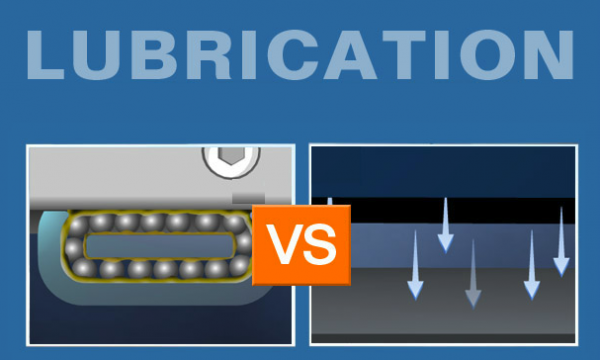
No Lubrication
Mechanical contact requires lubrication. Because conventional rolling element bearings rely on the movement of balls against a guide surface, lubrication is a standard part of ongoing equipment maintenance. But lubricant migrates to the guide surface, and also causes out-gassing, often effecting the process at hand or the environment. Maintenance is not only necessary, it can…
Acceleration
Conventional rolling element bearings are limited in their acceleration capabilities because of the rotating inertia of the balls in their guideways. These balls start and stop at inconsistent points. They slide, skip and skid. This causes precision problems, especially for applications with light loads over short distances. In a direct comparison, porous media air bearings…
Speed
There is an order of magnitude difference which separates the speed capabilities of conventional rolling element bearings from their porous media air bearing counterparts. Contact with the rail or guideway, and multiple different ball velocities, limit the speed capabilities of conventional rolling element bearings to 3-5 m/s. Porous media air bearings are a completely non-contact…
Smooth and Silent Motion
Any comparison with porous media air bearings must include a recognition of the constantly changing, multiple forces which act on the raceway integral to the function of the competitive rolling element bearing. The changing directions of the balls within this raceway result in velocity ripples which, in turn, compromise stability and impact performance. These velocity…
Zero Wear
When it comes to wear, contact is, again, the differentiating factor between rolling element bearings and porous media air bearings. Quite simply, balls show wear from mechanical contact. Over their lifetime, this causes friction changes, resulting in inconsistent machine characteristics. In fact, in mechanical contact systems, wear is a function of load, acceleration, velocity, distance,…
Zero Friction
The comparison between conventional rolling element bearings and porous media air bearings begins and ends with contact. Contact, and the resulting high stiction, often causes the rolling element bearing to overshoot its mark. This causes resolution problems, especially with light loads over short distances. New Way Porous Media™ air bearings are entirely non-contact, so there…
Learn More About the Porous Media Difference